Written By: Hari Koguru & Neelabh Ghosh
With emerging tech comes new risks; therefore, assessing and mitigating these risks is critical for developing a secure future. In 2023, the average data breach cost had increased substantially to $4.45 million. These alarming figures emphasized the need for the payment card industry (PCI) to enhance security measures. As a result, PCI DSS v4.0 was released in March 2022 by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC).
Who Should Meet The PCI DSS v4.0 Criteria?
Organizations that manage, process, or store cardholder data to safeguard and ensure the security of sensitive payment card data are required to meet the criteria of PCI DSS v4. This includes:
- Merchants: Businesses that accept credit cards online and in person, including retail establishments, restaurants, hotels, and e-commerce firms.
- Service Providers: Businesses who accept, store, and transfer credit card information on behalf of merchants. These include payment processors, web hosting providers, and security agencies.
- Financial Institutions: Credit card issuers such as banks and credit unions.
- Credit Card Payment Processors: Financial service providers such as Visa, Mastercard, American Express, etc.
- Other organizations: Organizations other than payment processors that handle card data, including cryptocurrency exchanges, healthcare providers, and educational institutions.
PCI DSS v4.0 Transition and Timeline
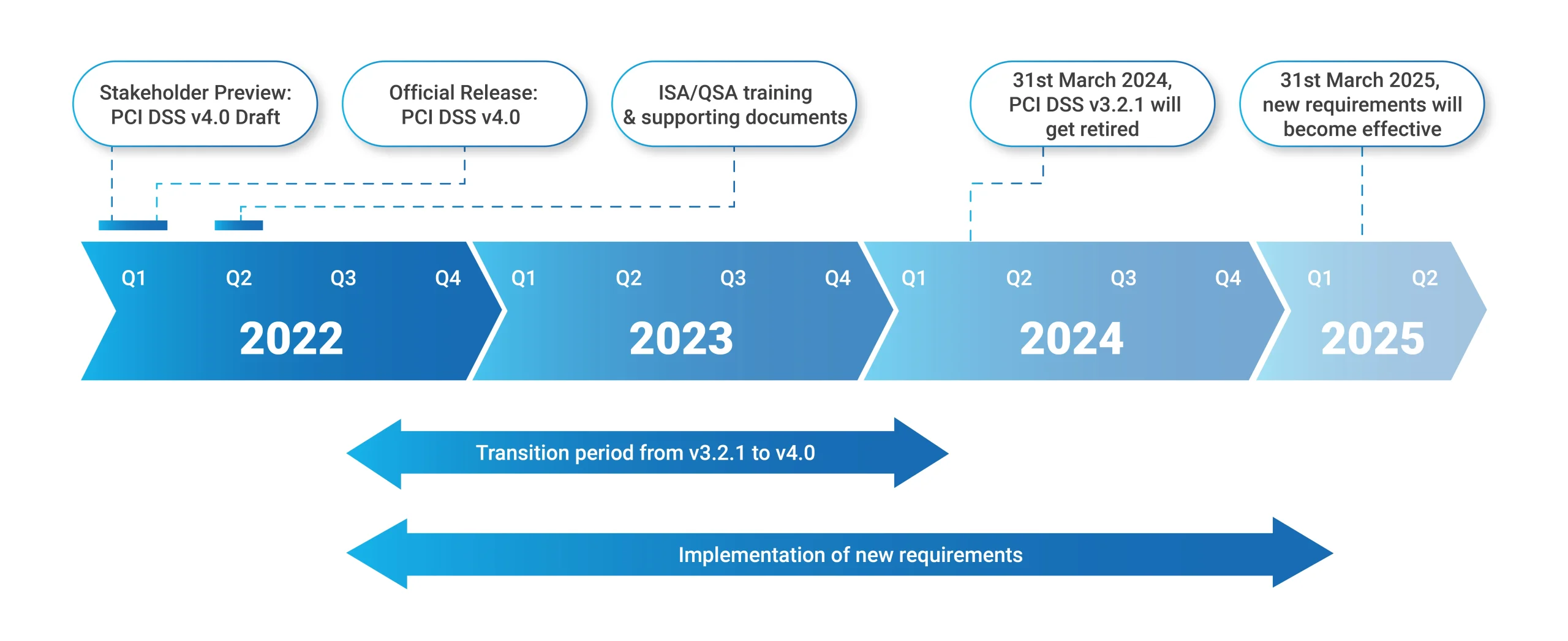
After the release of version 4.0, PCI DSS v3.2.1 will be maintained for two years. This transition period (from March 2022 to March 31, 2024) allows organizations to adapt to the changes introduced in v4.0. During this time, businesses can alter their reporting templates and forms to reflect the new standards and devise strategies to meet the revised criteria. It is crucial to highlight that on March 31, 2024, PCI DSS v3.2.1 will be phased out, leaving only v4.0 as the current standard version.
Four Major Reasons For PCI DSS Transition From v3.0 to v4.0
- To enhance the ongoing alignment of the standard with the evolving security demands of the payments industry
- To foster the idea of security as a continuous dynamic process
- To enhance the methods and procedures for validation
- To expand the framework’s flexibility and strategies for achieving robust security in the payment card industry
PCI DSS v4.0 Requirements
Key Focus Areas in PCI DSS v4.0
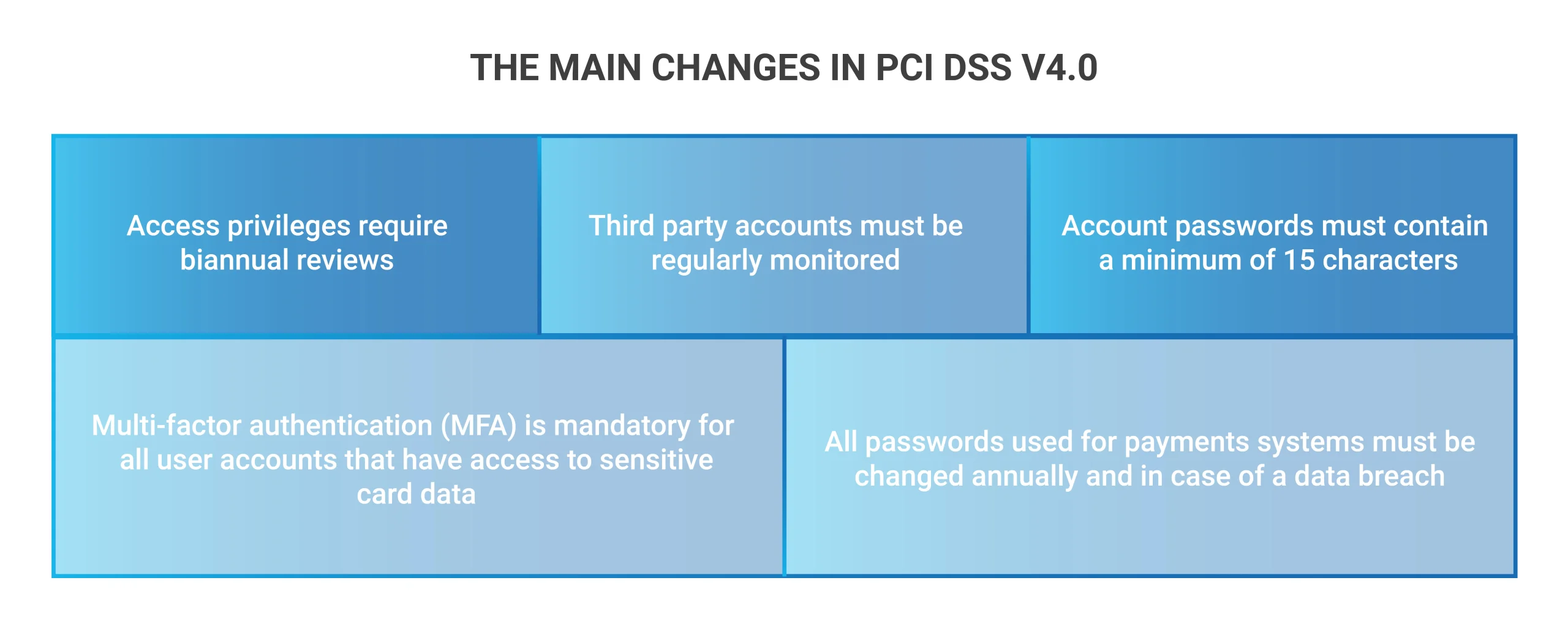
1.Stringent Authentication and Access Control Requirements: The newly upgraded PCI DSS, version 4.0, strives to promote security by implementing strict authentication processes and access control systems. Notably, using all remote access to cardholder data requires multi-factor authentication (MFA). This significant update also covers new role-based access control (RBAC) and privilege account management requirements, emphasizing the importance of effective security mechanisms protecting critical information.
2. Security Measures in the Cloud: PCI DSS 4.0 protects cardholder data in the cloud by incorporating more stringent security measures. It also involves strong encryption, cloud environment segmentation, and suspicious behavior tracking.
3. Strengthen Incident Response and Vulnerability Management Programs : Organizations must be pre-emptive and adaptable in protecting their business models. To align with the PCI DSS v4.0 standards, they must enhance their incident response plans and vulnerability management processes by conducting penetration testing, vulnerability scanning patching, and threat intelligence.
4. Emphasis on Zero-Trust Security: PCI DSS v4.0 addresses the zero-trust security principles to protect cardholder data. This entails developing policies requiring organizations to undertake measures including multi-factor authentication, micro-segmentation, least privilege access controls, and continuous monitoring in their Card-Data Environment (CDE). Adopting these approaches not only assists firms in achieving compliance but also minimizes risks of data breaches, improves incident response, and enhances security.
Steps To Prepare For A PCI DSS Audit
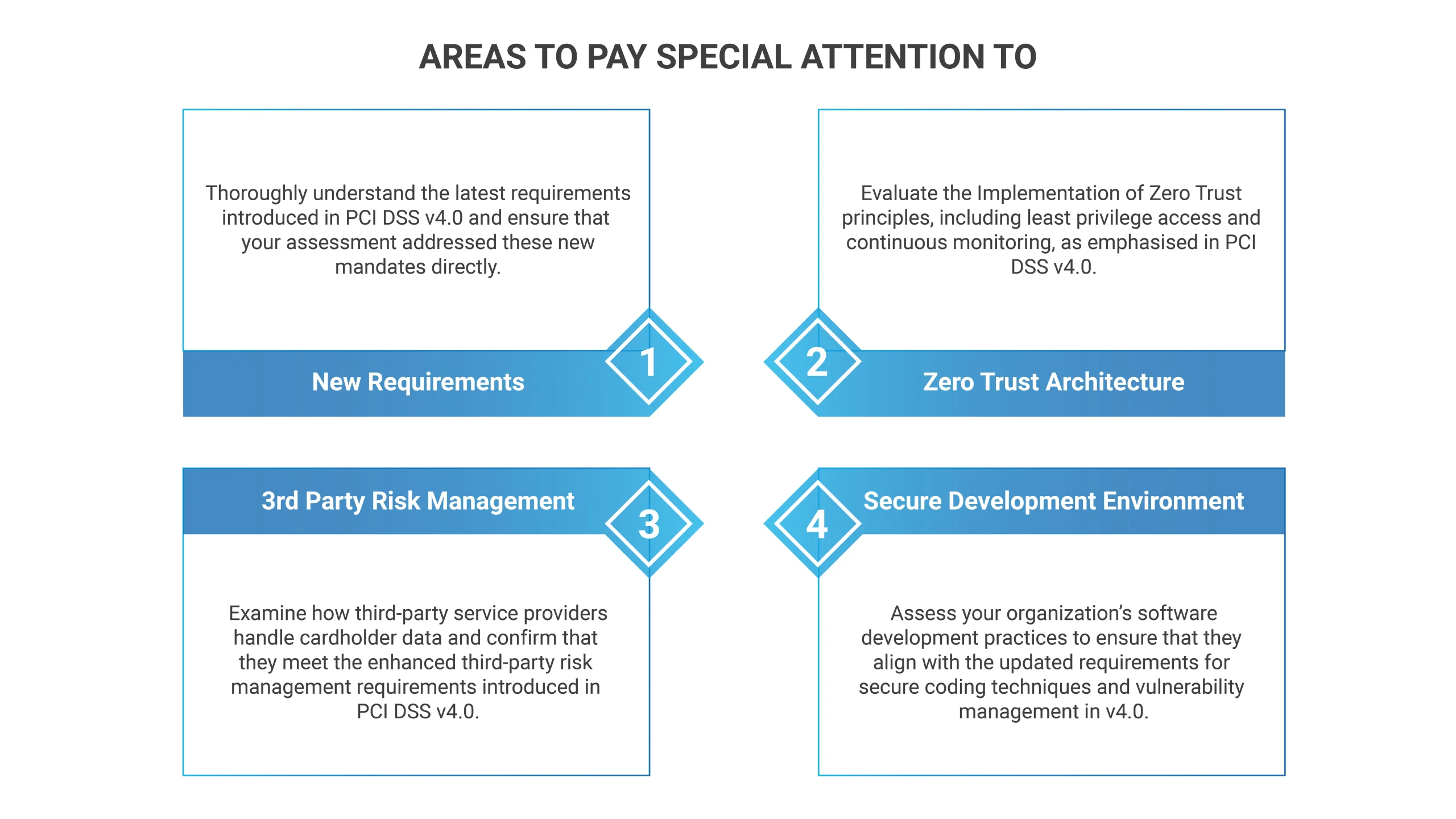
- Adhere to the Latest Standards
Businesses seeking PCI DSS certification must take a proactive approach. They must incorporate the new criteria into their operational environment while being cognizant of the existing ones. This needs a thorough evaluation and change of information security policy to reflect the changing regulatory landscape.
2. Cyber Security Risk Evaluation
A cyber risk assessment is instrumental in preparing for a PCI DSS v4.0 assessment by:
- Finding and prioritizing security perils to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Ensuring your current security posture aligns with the requirements of PCI DSS v4.0.
- Conducting risk assessment that aids the auditor with a clear understanding of any non-compliance as well as vulnerabilities identified and addressed.
3. Create Comprehensive Policies and Procedures
- Develop robust policies and procedures aligned with PCI DSS compliance.
- Clearly define how each requirement is met and ensure they seamlessly integrate with your existing security practices.
- Demonstrate organizational commitment to safeguarding cardholder data.
- Regularly review, update, and adjust documents to meet dynamic PCI DSS standards.
- Maintain consistency to uphold an effective and compliant security framework.
4. Monitor User Action Across All IT Infrastructure
For PCI DSS v4.0 certification, monitoring user activities throughout the entire IT infrastructure, including remote sites and mobile devices, is essential. This approach allows businesses to identify and investigate suspicious activities such as unauthorized access to cardholder data or attempts at installing malware. In addition, it allows for a quick response to potential data breaches and improves the security level by identifying areas where users act imprudently.
Furthermore, organizations can access several tools that can help them monitor user activities efficiently, such as SIEM systems and IDS or IPS. Collectively, these tools provide a comprehensive and real-time view of user activities throughout all IT environments.
5. Build Secure Partnerships
3rd-party service providers pose a significant risk to data security, contributing to many data breaches. PCI compliance mandates organizations to share responsibility for securing cardholder data entrusted to 3rd parties.
Here are a few methods to assess 3rd-party providers:
- Request AOC and ROC: Obtain their Attestation of Compliance (AOC) and Report on Compliance (ROC) for insights into security controls and PCI DSS compliance.
- Complete Security Questionnaire: Require completion of a security questionnaire to assess their security practices, providing a baseline for understanding their security posture.
- Engage a QSA Assessment: For the most comprehensive and in-depth evaluation, involve a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) to assess the PCI compliance with detailed reports.
Note: Consider the size, type, and complexity of the service provider
It is crucial to highlight that compliance isn’t a one-time process; it’s an ongoing process. Regularly reassess your partners through periodic questionnaires, spot checks, or renewed QSA assessments to maintain long-term security and minimize risk.
6. Secure Networks
- To adhere to the PCI DSS v4.0 standards, emphasize efficient network security controls, complete segmentation of networks, and strict issuance protocols for access.
- Perform ongoing security control monitoring and testing, audit systems, and collect data that must be secured within the PCI DSS scope, performing a comprehensive risk assessment.
- Establish an employee security awareness program with an effective incident response plan.
- Strengthen the network with key technologies such as firewalls, IDS/IPS, encryption, and multi-factor authentication technology SIEM systems web application Firewall (WAF) DDoS protection zero trust security. These measures collectively control access, safeguard against unauthorized entry and malicious traffic, encrypt sensitive data, contain breaches, prevent unauthorized access, identify potential incidents, protect web applications, and mitigate DDoS threats, ensuring alignment with PCI DSS v4.0 requirements.
Choose Accorian For Your PCI DSS Transition & Compliance
Accorian holds the prestigious distinction of having a team of highly Qualified PCI QSAs (Qualified Security Assessors) specializing in assessing PCI compliance, particularly emphasizing network infrastructure. We are also CREST accredited and an ASV (Approved Scan Vendor). Our PCI accreditations underline our expertise and credibility in cybersecurity and PCI DSS compliance.



