Written By: Vineet Kushalappa & Vignesh M R ||
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) aims to change how organizations oversee information protection and bind information protection rules throughout Europe. It was introduced in 2018, and considering its severe necessity of such a standard, its significance has monumentally increased. This blog deep dives into the elements of the GDPR standard, its significance, its many structures, and best practices to ensure compliance.
GDPR empowers individuals residing in the EU digitally by providing them with certain rights over the data collected and stored by organizations. It also enforces certain restrictions on organizations collecting and storing customer data, thus improving data security and dramatically reducing the chances of data losses and breaches.
Applicability of GDPR - Who Must Adhere to Its Regulations?
Contrary to popular belief, GDPR regulations are not limited to entities operating within the EEA (European Economic Area) but applies to any and every any organization that collects or handles personal data of EU citizens, regardless of its location. If an organization is located outside the EU but provides services in the EEA, it too must demonstrate compliance with GDPR.
GDPR regulations state that any entity or organization that collects, stores, transmits, and processes personal data is a Data Handler. Two types of Data Handlers are required to comply with GDPR: The Controller and The Processor. The term “Controllers” refers to people in charge of personal data. They can choose the purpose, means, use, and storage of data collection. Controllers may represent organizations, government agencies, or individuals who meet the prescribed conditions.
On the other hand, ‘Processors’ refers to those entities that handle, store, or process personal data based on the requirements set by the Controller. They are entities that provide services to controllers, such as data analysis, transfer of data, data destruction, and even storage of data. However, processors have restricted authority, meaning they can only act within the boundaries set by the controller and must adhere to the stated instructions.
Key Provisions of GDPR Regulations
GDPR is a regulation that has various articles and provisions to protect data. The following features play an important role in securing customer data. They are as follows:
The Business Advantages of GDPR Compliance Framework
The GDPR is a stringent data protection regulation that focuses on transparency and privacy by default. By complying with GDPR, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting users’ privacy. Furthermore, complying with GDPR can provide a competitive advantage for organizations striving to expand their operations in the European Union.
GDPR also helps streamline the businesses’ data management practices. Certain General Data Protection Regulation requirements or processes ensures that data is collected, stored, and processed in an organised manner which in turn helps organizations operate more efficiently and reduces the chances of potential data breaches.
Organizations can also maintain the security and integrity of their data cross-border by adhering to GDPR, which includes stringent requirements on transferring protected data outside the European Union. Cross-border transfers are crucial to businesses that export and import data. In order to facilitate them, GDPR has increased territorial reach beyond the European Union, ensuring that protected data is securely processed and stored by organizations outside the European Union.
Due to its international applicability, even organizations outside of the EU can benefit from aligning their data protection practices with GDPR. It can help organizations improve their global opportunities as the compliance standard enhance the organization’s reputation as a responsible and trustworthy entity.
Best Practices to Ensure Compliance with GDPR Regulations
Navigating the GDPR requires both best practices and specific compliance measures. The essential steps and practices for organizations to ensure GDPR compliance framework are as follows:
Conclusion
The following General Data Protection Regulation best practices are critical for the GDPR compliance landscape. While guiding through the GDPR compliance landscape, it is imperative for an organization to follow the data protection best practices. This helps organizations strengthen their compliance efforts by implementing robust measures, such as data processing protocols, open consent systems, frequent audits, and thorough staff training.
Accepting these practices not only ensures alignment with GDPR regulations but also strengthens trust with stakeholders by safeguarding personal data and supporting individual rights.
How Accorian Can Help
Accorian offers comprehensive GDPR services to evaluate and enhance an organization’s security posture. We provide meticulous gap and compliance assessments that delve deeply into GDPR requirements, identify potential risks, and safeguard sensitive data. We aim to protect brand reputation, financial integrity, and client trust by safeguarding sensitive customer data.
We recognize the importance of protecting an organization’s sensitive information. Our General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) services are thorough, reliable, and discreet, designed to safeguard your interests and build client trust. With our assistance, organizations can confidently adhere to GDPR, protecting themselves against potential disruptions, financial losses, and damage to their brand reputation.
FAQs on General Data Protection Regulation
Here are some frequently asked questions based on the General Data Protection Regulation:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) empowers individuals in the EU region by giving them certain rights over the data collected and stored by organizations. It also enforces certain restrictions on organizations’ collection and storage of customer data, improving data security and dramatically reducing the chances of data losses and breaches.
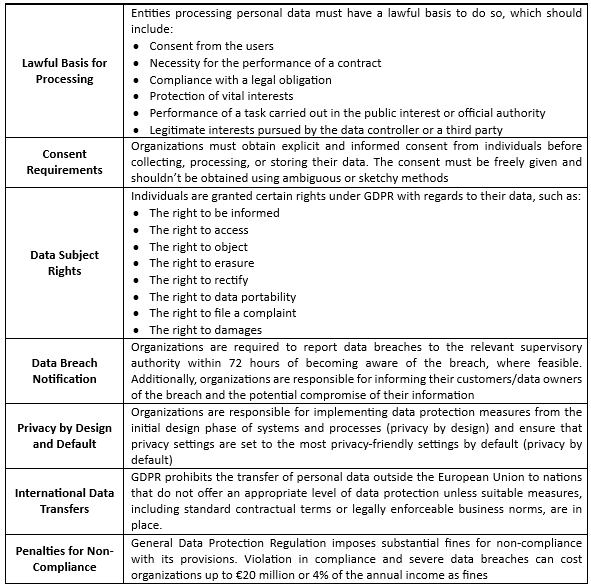
The 7 key articles of GDPR are as follows:
- Lawful Basis for Processing
- Consent Requirements
- Data Subject Rights
- Data Breach Notification
- Privacy by Design and Default
- International Data Transfers
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
GDPR is not limited to entities operating within the EEA (European Economic Area). It applies to any organization that collects or handles the data of EU citizens, regardless of its location.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) enforces strict data protection, focusing on transparency and privacy. It enhances competitive advantage in the EU, reduces breach risks, ensures safe data transfers, and boosts global brand reputation and market access.
Appointing a Data Protection Officer is essential for organizations handling large-scale processing of sensitive data. DPOs are the main point of contact in implementing and managing the organization’s security posture. They are responsible for ensuring that the organization stays compliant with General Data Protection Regulations via various activities, such as internal audits and compliance activities.


